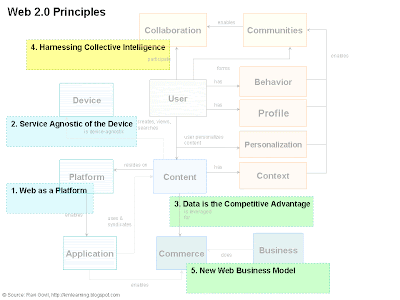
In my previous post, I had demonstrated the conceptual model of web 2.0 that shows all objects and their relations. It is high level visual representation of web 2.0 object graph. In continuing with the concept, I am trying to map these objects with web 2.0 principles and technologies in this post.
The key principles of web 2.0 are:
1. Web as a Platform - It is a large single market place with over a billion people using it. It is primary global store for the software and data. Over last few years more and more product and services are getting integrated and available on the web. The web grew at the same rate as the technology advances in network bandwidth over the period of time. The higher network has become faster and cheaper, has been widely adopted during this period. Now more and more software are available on the web as services and are getting integrated with main stream applications.
2. Services Agnostic of the Device - In web 2.0 era, the applications and content are designed to be delivered across devices so that it can be accessed from anywhere, anytime. More so now the content and services resides in the cloud. In web 2.0, device does not constraint the services but embraces it.
3. Data is the Competitive Advantage - Organizations are leveraging the data and content for creating new business models. Now not just the software but also data is great market asset. "Data is the the new intel inside". Companies like Google, Youtube, Linkedin leveraging the data to create new innovated services and business models on the web.
4. Harnessing Collective Intelligence - Next generation application are now more user centric rather process centric. End user is no longer just a consumer but also a partner, empowering them to improve the products and services. The focus has been shifting from command and control enterprise culture towards collaboration and teamwork. The end users create the network effect.
5. New Web Business Model - Web 2.0 advocates opening your platforms to others, integrating other applications to bring more value to en users and business.
Other than those mentioned above, there are additional principles which are more pertinent toward delivery and user experience. Though these existed in web 1.0 era but were not that important and were not major constraints to the apps. For instance..
1. Rich User Experience
2. Continuous and Incremental Releases
Now I will classify the web 2.0 technologies with respect to the conceptual model, where and how these technologies fit together.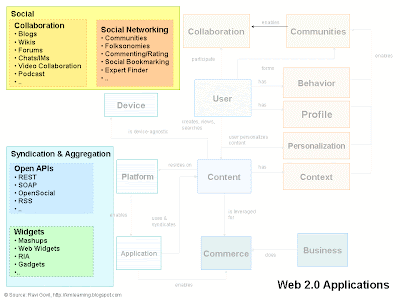
1. Social - The social apps can further be classified into collaboration and social networking. Some of the collaboration applications are blogs, wikis, forums, chat, podcast etc. Some of the social networking applications are social apps, folksonomy, social bookmarking. Though I have seen lately these applications are merging into a single platform.
2. Syndication and Aggregation - Some of the apps in this category are RSS, REST, OpenSocial, mashups, web widegts, RIA, gadgets.
Please let me know your comments about the web 2.0 conceptual model and its mapping with principles and technologies.
Additional Links
1. Web 2.0 - Conceptual Model
Friday, May 16, 2008
Web 2.0 - Conceptual Model (Part 2)
Tuesday, May 13, 2008
Web 2.0 - Conceptual Model
There are as many definitions of web 2.0 as number of people. Everyone creates their own definitions based on their requirements, understanding and budget at hand. Initially Tim O'Reilly defined web 2.0 as applications that leverage network effects and proposed seven
principles. Those principles still remain the governing definition of web 2.0 even today. That said, how about defining web 2.0 in a conceptual model? A definition which everyone can understand, has one language and is visual.
There are some interesting concepts I came across to define web 3.0 at Sramana Mitra's Blog. It talks about web 3.0 in terms 4C's, P and VS. 4C are content, community, commerce and context. P is personalization and VS is vertical search. Very interesting explanation of the
concept.
I have tried to come with a conceptual model of web 2.0. This is still working document and I plan to extend it with some feedback from you all. The conceptual model consist of set of objects and their relation, governed by web 2.0 principles and enabled by web 2.0 applications.
Web 2.0 advocates "data is the Next Intel Inside" i.e. Content is processing power of the web. User pulls the information all the time, anytime and anywhere. User views the content in Context of his intent. User also personalizes the information based on his interest.
Content resides in the cloud and is agnostic of the Device. It can be created and viewed from any device. Content should be used as competitive advantage for the Commerce. For example, Google search engine uses indexed content as an advantage in monetizing through adsense and adwords. In 2.0 era, web is seen as a Platform that enables Applications, repository of data and enables integration with other systems.
Web 2.0 encourages team work, collective intelligence and building Communities. We have seen applications like Facebook, MySpaces etc. have so many communities, networks and groups. Building of communities can leverage data from user Profile, his Behavior, his personalized information and his information context. Communities enable team Collaboration and Communication , knowledge sharing and team workspaces.
I am working on this web 2.0 conceptual model and will map this model with the web 2.0 principles, and technologies and applications in next post.
Additional Links
Sunday, May 11, 2008
Enterprise Mashup Market expects to grow to $700 million by 2013
A new report released by Forrester Research is predicting that enterprise spending on Web 2.0 Mashups technologies is going to increase dramatically over the next five years and expect to grow to $700 million by 2013. This means that there is plenty of money to be made selling mashup platforms, it will affect nearly every software vendor. Mashup platform will get lot of attention and vendors are gettingready to get their pie of share in growing mashup market. The mashup platforms will leverage new emerging mashup technologies and data provider APIs to provide next generation enterprise applications. Now it is time to vendors to quickly work on new strategies, new technologies and new partnership alliances to come on the top.
Report distinguished between enterprise mashups and those in the consumer space. Consumer mashups typically are built by a individuals or consumer space vendors. In the enterprise space, mashup be lot more challenging since it needs to pull data from diversified portfolio of applications. The challenge would also be able to provide this information in a meaningful and intuitive way. It will be difficult for the enterprises to build these mashups on their own without the help of mashup platforms and mashup experts. According to the researchers, vendors will provide tools for business users to build a mashup on their own with no programming experience.
In April 2008, IBM announced the beta version of IBM Mashup Center. The IBM Mashup Center consists of two tools — Infosphere MashupHub and Lotus Mashups. This announcement follows an earlier one made on 3 March 2008 about WebSphere sMash. The three offerings are related, but enterprises can purchase and use them separately.
Some of other mashup platforms are JackBe, Kapow Technologies, Microsoft, Serena Software, Strikeiron, and XigniteTuesday, May 6, 2008
Folksonomies - Collaborative Tagging
This posts explains the user-defined collaborative tagging and how it is applied to organize and share information. And it will also provide ideas around the information classification to achieve search and retrieval faster and more efficient and relevant.
Metadata by definition is "data about data", basically adding more intelligence to data and establishing better relation between pieces of information. Metadata is usually created either by professional taxonomy experts or content authors. First method is very expensive since it involves formal taxonomies and controlled vocabularies. Besides it's even impossible when you have large legacy data which is yet not tagged. Second method overloads the authors with additional tasks and requires an understanding of metadata tags. These approaches are still disconnected with the end users because it does not understand the intent and context of the end user. Though the methods help in searching the relevant information faster and easier through search and taxonomy navigations.
Third form of tagging is called user created collaborative tagging i.e. folksonomies. It is also call community classification of information another aspect of social networking. Google has used an approach of collaborative classification in page ranks using PageRank algorithm. The number of links pointing to a web page allows Google to optimize its search relevance and rank the page appropriately. It is another form of implicit user created collaborative classification of information. Amazon has used customer reviews effectively to add intelligence to catalog, another implicit form of classification.
Social Bookmarking employs explicit form of user created collaborative tagging. Sites like Del.icio.us, Digg, StumbleUpon etc. provides ability to bookmark your urls or sites and create additional tags to the urls. These tags are created by end user in context with the intent and usefulness of the site. They also allow users to describe and organize content with any vocabulary they choose. It is completely disconnected with the owner and author of the information. In addition to automatically generated chronological ordering of bookmarks saved to the system, the tags are used to navigate the bookmarks within a user’s collection. Additionally, these tags are also used to collocate bookmarks across the entire system, so for example, looking at the page http://del.icio.us/tag/web2.0 will show all bookmarks that are tagged with “web2.0” by any user. Functionality of these social bookmarking sites varies from one another but the basic idea is the same, ability to tag the urls and be able to share across the system.
Although folksonomy is not a controlled vocabulary, and does have limitations, there have lot of advantages that bring lot of value in sharing, collaboration and social networking.
Finding the information faster - In order to find the a relevant content, one has to browse the websites or search through the web search engines. At times exploring the bookmark tags in the social bookmarking sites, one can find many recent resources from a wide variety of authors and sites that likely would never have been visited before. There is a fundamental difference in browsing the tags to find interesting content, as opposed to searching to find relevant documents in a query. The other users have found these content items or sites relevant and useful, so it is higher in relevance optimization.
User centric vocabulary - most important strength of a folksonomy is that it directly reflects the vocabulary of end users. End user can tag the information based on intent and context of the information, not based on the intent of author. In fact it is not derived from taxonomy expert or intellectual property producers or information owner, but from the consumers of the information. In this way, it directly reflects their choices in terminology and language.
Limitation of folksonomies are mostly user centric and system confined, and by no means limits the use of the system.
Uncontrolled vocabulary - Ambiguity of the tags can emerge as users apply the same tag in different ways. There are no explicit systematic guidelines and no scope notes.
Structure of tags - structure is usually single word with no spaces, sometimes makes it difficult to merge various tags. For example web2.0, web2, web20 means the same tag but would show as separate taxonomy nodes.
Semantic tags - There is a limitation of synonym words in the system as tags are user generated. For example, web and www should be classified under same tag.
Social Bookmarking sites have extended functionalities of folksonomy with social aspects like commenting, rating, community building etc. In Digg, one can start a feedback loop on tagged content and also see who all have tagged this content. In addition, communities can be build using data collected on the social bookmarking sites.
The folksonomy can be used in enterprise 2.0 to supplement existing taxonomies and provide additional access to materials by encouraging and leveraging explicit user generated tags. If enterprises begin to incorporate user-centric information management systems, the folksonomies developed by the users have great value in information sharing and retrieval systems.
Monday, May 5, 2008
What Is Enterprise Web 2.0 Software?
Interestingly someone asked this question on linkedin. This question has been asked to me by many people who have limited understanding of web 2.0 and trying to adopt web 2.0 in the enterprise environment. Some of them even ask how many softwares they need to buy or build to enable enterprise web 2.0. Then I have to explain them the basics of web 2.0 and what is required to adopt web 2.0 within the enterprise.
Before we get into enterprise web 2.0 software, we need to understand what is web 2.0. It is not just a technology, it's a trend. Web 2.0 is built on set of principles that differentiates it from legacy paradigms. The principles including using web as platform, using company data as business advantage, having apps which are device agnostic, apps with rich user experience, apps harnessing collective intelligence, and apps that are lightweight ever evolving enabling new business models. They must leverage network effect. Web 2.0 applications need to provide business value, either in additional revenue or reducing costs. If one looks at these principles, any application which is build on one of these can be classified as "Enterprise Web 2.0 Software".
For example, one of the principles is harnessing collective intelligence, it is basically team collaboration, knowledge sharing and team workspaces. Wikis are one of the most widely adopted web 2.0 collaboration technology. Its been used for knowledge sharing, project management, task management and online collaboration with team members. Wikis can be classified as "Enterprise Web 2.0 Software". Wikis such as eTouch SamePage, Confluence, MediaWiki, ClearSpace have got lot of traction from the enterprises. Another example, in search domain there are products like Baynote which enables relevance optimization on the legacy search engines. They leverage end users behavior and their clicks, to generate better relevance on search engine results. They are also classified as "Enterprise Web 2.0 Softwares".
There is no single product that claims to solve all business problems and at the same time enable web 2.0. It is how you implement and deploy these applications and bring value to your business. It all depends on your problem and the business.
Wednesday, April 23, 2008
Implementing Web 2.0: Practical Approach
Knowledge of web 2.0 is key for decision making and strategy building for embracing, provisioning and adopting web 2.0 within the enterprise. But knowing does not always translate into doing it. Web 2.0 is not just about technology, it is about people, processes, cultured and, change and adoption. It is about business strategy, value proposition, and competitive advantage. It is very critical for organizations to implement right and effective implementation methodology to deploy web 2.0 applications in the portfolio, measure return on investment (ROI), and build and sustain competitive advantage.
People drive the vision, commitment, change, and culture. The organizations can only create environments to realize these visions. Vision is not just aligning the thoughts with business drivers, but also introducing new ideas and new initiatives. Not all initiatives see the light, success and adoption, commitment is the black bone of all implementations. Web 2.0 is also intertwined with the change in processes and culture. It is destructive model requires realigning to newer processes, technologies and business strategies. In order to be accomplish your vision, you need a well-thought proven methodology to succeed.
Many organization have adopted web 2.0 principles not as a business strategy but more as an experiments to get on the web 2.0 technology map. These companies are plying low risks strategies and trying to gauge its adoption with respect to business model and corporate culture. Others are still in wait and watch mode, closely monitoring the web 2.0 adoption and success within the enterprise, waiting to see if the Web 2.0 bubble is bursting. If the bubble does not burst as it looks like, these organization will lag behind others who adopted it whether successfully or not.
The web 2.0 implementation methodology framework consist of six stages. It is education, strategy, planning, implementation, adoption and measure & improve. Though it is typical of any methodology to have these stages, but it is important to understand each of the stages in web 2.0 implementation.
The key activities in each of these stages are listed below:
Education
- Understand Web 2.0 principles
- Enterprise 2.0 Trends
- Applying Web 2.0 to your Business
- Formulate Web 2.0 Vision
- Assess Competitive Advantage
- Strategise Business Transformation
- Implementation Roadmap
- Technology Selection
- Project Methodology
- Software Design
- Application Development
- Deployment & Support
- Community Engagement & Mgmt
- Leading Organization Change Mgmt
- Executive Management Commitment
- Measure Web 2.0 Maturity
- Gap Analysis & ROI
- Review & Plan
Please feel free to comment on this posts.
Monday, April 21, 2008
Expect $4.6 Billion In Spending By 2013 As Large Companies Embrace Web 2.0
A new report released today by Forrester Research is predicting that enterprise spending on Web 2.0 technologies is going to increase dramatically over the next five years. According to the report, enterprise spending on Web 2.0 technologies will grow strongly over the next five years, reaching $4.6 billion globally by 2013, with social networking, mashups, and RSS capturing the greatest share. Enterprise web 2.0 tools will be adopted, provisioned and embraced by the enterprises over the next five years overcoming all the challenges of technology, monetary benefits, business market and corporate cultures.
Web 2.0 market place is divided into consumer and enterprise services. Consumer services includes Myspace, FaceBook, twitter etc., targeted towards consumers, monetized through ads and evaluated based on traffic. The consumer services are part of enterprise services.
Enterprise services have two aspects - Internal and External. Internal aspect is aimed at the employees, internal communication, knowledge sharing and product innovation. External aspect is geared towards customers and partners, marketing and sales, product development, customer services and retention, and new opportunities.
This reports covers some of the most compelling questions. What Is Enterprise Web 2.0 Software? Can Software Firms Make Money Selling Enterprise Web 2.0 Tools? And talks about external and internal facing markets and how it will be driven.
Overall the reports align with the trends in the market place. Enterprises are keen in adopting web 2.0 principles in both external and internal aspects. Knowledge Management is being replaced with web 2.0 collaboration and social networking applications. The executives understand the need, but knowledge of web 2.0 and how to implement is still missing. They are opting for less risky web 2.0 pilot applications instead of realigning their business strategy with web 2.0. But I am sure success of pilot applications will lead to bigger initiatives. It is just a matter of time and confidence.
There is lot of scope of ideas, technology and services for all product companies, service providers and enterprise IT teams in coming years. The web 2.0 products who have not yet seen the light would reap benefits from the enterprise adoption. Service vendors who have knowledge of web 2.0 and their challenges can take advantage of web 2.0 deployments and create a niche market for themselves. The enterprise IT team will either have to consolidate their ideas and resources or outsource the new initiatives in web 2.0. But in the end, it will be win-win situation for all players in the web 2.0 space.
Wednesday, April 9, 2008
Web 2.0 - Challenges in Enterprise Deployment
Web 2.0 offers business opportunities, but brings challenges in how corporations embrace community, approach the sharing and protection of proprietary information, and identify and exploit its value. The challenges and issues that web 2.0 presents to enterprises can not ignored before deciding on adopting it. Web 2.0 still inherits all the challenges of traditional web application development and delivery. That includes project management challenges i.e. requirement, budget, schedule, resources, qa etc. and also technology limitations like scalability, interoperability, security, development methodologies etc. But if the challenges would have been same as that of any web application development, why web 2.0 applications have not yet been widely deployed in the enterprises.
After working with some of the large enterprises in last few months on web 2.0 initiatives, I have some ideas on challenges that have been faced by these companies. These challenges are very specific to web 2.0 and its principles, and can not be applied to traditional web development.
The biggest challenge of web 2.0 application delivery is adoption. Adoption by the corporate, technology and people.
Every corporate has it own culture, way to doing things and getting the things done. The culture is deep routed and depends upon the how old the company is. The old corporate houses have more issues with the culture and the changes in comparison with new startups. The new initiatives face cultural resistance from some class of users, for example, clinging on e-mail and other traditional tools for collaboration rather than switch to new Web 2.0tools. The biggest challenge is overcome this cultural resistance. Some employees feel insecure whenever there is change, be it fear of loosing their job or working additional hours on new technology, while some do not want change since they fear it may be effect their efficiency or they are contented with their way of working. Now question is how to overcome this resistance. Web 2.0 evangelist and proponents have suggested both top-down and bottom-up approaches for corporate adoption.
Technology selection plays an important role in any application deployment. Which technology should I use? What is life span of this technology? Am I locking myself into a vendor proprietary technology? One needs to answer these questions before selecting any technology. Now in last few years there are two distinct perspectives that have emerged and are conflicting. One perspective is selecting technology from a vendor who has not only pioneered but also has sustained business, for example, say Microsoft or Oracle. Other perspective is using open source technologies and building stack of products on top of that. Both have pros and cons, depends on where and how it is being used. Thanks to web 2.0, now more and more products remain in perpetual beta. Would you choose a tool or technology for an enterprise that is in perpetual beta? Would I be able to convince my management to invest in technology that is not yet officially released? Companies are confused in selection of technologies, option to choose from vendor proprietary or open source applications and frameworks.
The second biggest challenge is adoption by the employees of company. These days employees spend more time with web 2.0 applications, for example, FaceBook, Linkedin, MySpace outside the office environment than they do within the office. They are smart and intelligent people. They are aware of social networking application features and are also aware of engaging user experience that consumer web 2.0 applications provide. Their expectations have gone up and now they want similar applications to be deployed in their office environment. They will not accept anything that is not close to the application they use.
Web 2.0 advocates moving away from command and control towards collaboration and teamwork, from push to pull model, from process-centric to people-centric business model. The organizations that believe in command and control culture would require self assessment and strategic change toward collaboration and teamwork culture. It requires executive sponsorship and corporate cultural change.
The popularity and adoption of web 2.0 and agile development methodology happened around about the same time. There is a reason for it. In the Web 2.0 era, products and services are really never finished and must continuously improve to compete. They remain in perpetual beta. This is against the definition of the project, it has a starting date and fixed end date. Web 2.0 applications are continuously evolved and improved and end user are part of large testing team. This requires change in development methodology of web 2.0 applications. Some call it web development 2.0 but it is nothing but agile or scrum methodology. The scrum methodology has become very popular in last few years and has seen widespread adoption in the enterprises.
Security is also a major challenge in web 2.0. The issues around privacy information, corporate asset protection, spam protection and digital rights management are very critical and need to be addressed. This requires additional budget and policy formulation, which are additional overheads for the company.
The question that is asked so often is, what will happen to the existing applications and how those can be leverage in web 2.0. It is not possible to replace all the existing applications with web 2.0 and it does not make any sense. Not all applications needs to be upgraded to web 2.0 since they do not add value of the network effort. But there is possibility where the data from these applications may be required in new web 2.0 apps. The challenge is how to integrate these applications. The mashups and API integration are two ways in integrating existing applications besides conventional url integrations.
I am sure there are other challenges in web 2.0 deployment within the enterprise. These are some which I heard from clients and web 2.0 pundits. Please let me know if you know of others.
Tuesday, March 25, 2008
Mashup - Web 2.0 with Enterprise (Part 4)
Web 2.0 is not a buzz anymore, has been widely adopted and results have been too encouraging in the consumer world to discard it as just another fad!! Business is also slowly adopting web 2.0 in both their internal and external applications. If you see, technology has taken time to mature always before it gets widely adopted. We have seen it with SOA and SaaS, it was seen as next generation application architecture by modern day architecture gurus. But it has taken time to mature and embraced by large majority of business and makes effective use of it. There have been some rumors of web 2.0 bust and also of next generation web 3.0. I do not want to comment on it yet because I think it is too early to reject web 2.0 and its potential has not yet been realized. I have seen in last six months that there has been shift in business serious dwelling in web 2.0 ideas and trying to leverage network effect of web 2.0 in their business model.
I have come up with a summary table of what web 2.0 applications are and how they can be used in the internal and external applications. Please feel free to comment.

Saturday, March 15, 2008
Mashup - Web 2.0 with Enterprise (Part 3)
In the previous post, we looked the web 2.0 applications that can be deployed with the enterprise for their employees. It is a misnomer that web 2.0 applications can either be consumer applications or internal applications within the enterprise. Companies are now taking advantage of the powerful web 2.0 concepts in streamlining their business models and processes. They are realizing that web 2.0 applications can be used effectively to engage, interact and support the customers, partners and suppliers to gain an edge in their business. Companies are looking for innovative ways beyond software creation and are engaging large communities of people on the web to participate in their business that was not possible before. This may require them to change their business models, though not necessarily in a disruptive fashion, and may impact their short and long term objectives and businesses. The web 2.0 applications have already shown results for some of businesses who have taken risk and plunge into the web 2.0 hype.
Everyone would ask the same question when it comes to adopting a new technology or a new paradigm. How would my business benefit from it? And the answer would be "it will help in increasing your revenue and reducing costs". No marks for right answer please. Aren't these the only two drivers for running any business? The question is "how can web 2.0 enable it - increase revenue and reduce costs". Research companies have done numerous surveys that have given them some insight into what C-level executives think of web 2.0 and how web 2.0 can help them achieve their business goals. Some of reasons for adopting web 2.0 in their business are acquiring new customers, customer service and support, product and service innovations, customer retention, online sales, and marketing, advertising and public relations. Most of the senior executives have been struggling to answer as to how and how much time it would take to see the results. Everybody's business is unique and it will take a thorough discovery cycles to identify what processes can be enabled using web 2.0 principles and what benefit they would reap.
Let's now look at some of the web 2.0 applications that can be used within the enterprise for external audiences, including customers, partners and suppliers. We will also see how they will benefit their business in providing them with engaging, lively and interactive alternative.
Businesses in general have been collaborating and communicating with the customers, partners and supplier. They have been doing this either through offline modes of collaborations like mails, phones, faxes or online mode using simple web applications to complex large portals. The offline modes of collaboration may be more personal but at the same time more expensive. As people are becoming more web savvy, they want all interaction to happen either through web or smart phones. Companies spend a fortune in this mode of communication. The legacy online collaboration used to happen through unidirectional web i.e. business would typically provide the content or data for the customer and supplier to view. But if they had a specific request for a service, they needed to revert back to offline collaboration i.e. pick up a phone or send an email. With the advent of web 2.0, the paradigm has shifted to read-write, user driven intelligent web. The customers and partners are more than willing to collaborate over the web. In addition, they can access the content on their PCs and smart phone and that too when they want it. Wiki is best tool for collaboration now. It provides all the rich features and functionality that is required for collaboration and communication including content creation, feedback, calendar, forums, project management etc.
Another usage of wikis are in creation of company-pedias. Companies can create wikipedia like company-pedias to distribute their products and services information and also enable customers, partners, and general audience to participate. This will enable to consolidate products and services information, success stories, case studies and white papers and create a knowledge repository.
Blogging is a tool for initiating a dialogs with rest of the web and get feedback from interested audience. The conversation is started typically by individual contributor and enables others to participate in it. Lately blogs have been extended to project teams where team members can write posts on the same blog about their works. Businesses have realized that this could be another effective tool for initiating conversation with the untapped large audiences on the web. It is not just limited to the untapped audiences but can also be used effectively with the existing customers and partners. Whether they are doing this still remains a questions? Yes, there is potential in using blogs as next generation tools in engaging and interacting with last user community on the web. In my opinion, most businesses should be active in exploring business blogs to communicate and collaborate with the customers, partners and untapped web community.
Web 2.0 is synonymous with social networks. Social network applications enable individuals to establish and maintain relationship on the web. The actions and functions of social network depend on the application and its objectives. It is also targeted toward specific audiences. MySpace, Facebook and Linkedin are the most popular social networking applications and are targeted toward different type of audiences. How different are these web 2.0 social networking applications from web 1.0 groups? They probably solve the same purpose but social network applications are much richer in functionality, are extensible and provide more engaging user experience. If you look at FaceBook, it provides extensibility by add-on applications which groups have failed to provide. The social networking applications can be used effectively in businesses in creation of online customer and partner communities. Such communities will be a great forum for exchanging information, ideas, reviews, feedback, recommendations, sales opportunities and support.
There are other applications like mashups, podcast, directory services, and RSS which businesses can leverage to enhance collaboration, communication, and content distribution. Besides companies are also adopting consumer targeted social networking applications like Linkedin, FaceBook in their businesses for creating business communities.
Tuesday, February 26, 2008
Mashup - Web 2.0 with Enterprise (Part 2)
Continuing my discussion on web 2.0 in an enterprise from the my previous post, now lets look at the some web 2.0 applications and how they have been deployed in enterprise environment.
Web 2.0 applications can provide value to the employees in internal collaboration & communication, knowledge sharing and collective intelligence. But we still need to answer some of the questions. How are these web 2.0 applications different from legacy applications? What additional value do these apps provide which the predecessors have failed in? I would say legacy apps have been very useful and provided everything that one needs. But now employees need more in web era.
Does company provide its employees with all the information and tools that I need to perform my daily job? Are they spending their working time in finding information that they should have readily accesses to? The shift in web 2.0 paradigm is to be able to pull the information anywhere anytime and more so when is required, rather than pushing information to the employees. The focus should be to transform the company’s tacit knowledge into explicit knowledge continuously and at all the times. The focus should be able to find the right experts when you want to connect with them rather than later. The focus should be able to harness collective intelligence of employee pool rather than handful of strategist. The focus should be on leveraging company data as competitive advantage in their business model. And apps will also enable business growth and reduce redundant cost.
Lets look at some of the internal apps and how they can help organizations in achieving their goals using principles of web 2.0.
Wikis are probably most used web 2.0 application with in the enterprise environment. The very reason for its popularity could well be the meaning of the word wiki itself, which is Hawaiian for "fast". Yes, it is first version of writable web. In comparison with traditional content management systems, wiki enables everyone to be able to manage content. It does not require elaborate complex processes to create and publish content, the user can edit the content in context and publish it. Wiki is a powerful tool for internal and external collaboration & communication including discussion threads, calendars, RSS, project management, knowledge organization, document management and much more. In fact it can be classified into platform category since it provides extended capabilities of mashups, data aggregation and integration plugins. Some of the most popular commercial wikis are SamePage and Confluence. There are tons of open source wikis that corporates can deploy if they happen to have even slightly strong IT teams. Do companies need expensive and complex Content Management Systems after advent of wikis? I guess not.
Collaboration 2.0 is another offshoot of '2.0 era'. These are platforms that have been built by integrating various related technologies that either existed standalone or built over them. This 2.0 platform is very much in space of wiki but more complex and controlled. It includes workflow, business intelligence, forms and email synchronization in addition to wiki features. Microsoft Sharepoint, EMC eRoom and Vignette Collaboration most popular tools in this space.
Expert Finder or Directory 2.0 puts enterprise on the social networking technology map. If you look at the traditional directory services within the corporate,
it is more like a contact list of the outlook application. In the web 2.0 era, when we are talking about harnessing collective intelligence and finding right connection at the right time, the question is, how do you know if the required expertise exists within the organization or not. It can further be extended into a social networking application where employees can create communities and collaborate on subject of common interests. Employees can cut through the red tape and connect with each other to reduce duplication of effort and collaboration.
Blogs have made millions of journalist out of common people. Anyone who has ideas and thoughts can share it with anyone in the world and get instant feedback. There is no more dependency on print media or web sites to reach out to people. Anyone can start blogging in matter of minutes and has million of readers at his disposal. Blogging is one of great tools for harnessing collective intelligence using comments. Techcrunch is one of the most popular technology blog in the world. In the enterprise environment, it will take sometime before free employee blogging will acceptable to everyone in upper management and become part of corporate culture. I have seen executive management blogs in most of the large corporates, a channel for information distribution. Blogs have been extended where ideas get posted through audio and video media. Podcast has added another channel for information distribution and has been utilized for trainings and information sessions.
Knowledge is key when it comes making strategic decisions. Knowledge needs to be created, shared, distributed and applied continuously within the organization. In web 1.0 era, knowledge was created by few and then distributed across through multiple channels, for example, MSDN. With web 2.0, knowledge is created though collective intelligence. Take an example of wikipedia, the largest knowledge base on web, is not created by few but by everyone who has the knowledge and are willing to share. How we can replicate the success of wikipedia in the enterprise environment? Wiki is the defacto tool for creating knowledge repositories within the organization harnessing collective intelligence.
RSS has become backbone of content syndication and distribution. It is as simple as it names suggests, real simple syndication. As mentioned in my previous post, web 2.0 applications leverage the network effort. Information has limited utility if it is not shared and distributed. Information needs to be distributed across the network so that it can be utilized appropriately to achieve better results. RSS can also be used to aggregate the data from various sources to create an actionable knowledge base.
How about we integrate all the web 2.0 applications discussed above in unified connect platform. Unified Connect is a collaboration and communication platform that takes care of all business needs. It includes all the collaboration applications including instant messaging, calendar, meeting place, document management, wikis, blogs, etc... New applications can be added to the platform using mashups and SaaS. Some of the products that are available to look at are from Cisco's WebEx and Adobe.
Tuesday, February 19, 2008
Mashup - Web 2.0 with Enterprise (Part 1)
Web 2.0 has been great success story with consumer products but much has still not been said or done with it in the enterprise environment. Pundits and analysts have been toying with idea of web 2.0 in the enterprise sector but surveys show very little actual adoption of web 2.0 in this area. How can the trends be optimistic if surveys show the opposite? The trends have been optimistic but actual implementation of web 2.0 is yet far away from reality. Do we know why?
What is web 2.0 in an enterprise? What do we need to know about web 2.0 that can be applied in an enterprise environment? Web 2.0 is a trend or paradigm that is shaping the next generation of world wide web. But this definition is not enough. Web 2.0 has different meaning for different audiences - technical and business. For technical community it is wikis, blogs, RSS, podcasting, folksonomy, mashups and social networking. From business prospective it is finding new business models and opportunities, marketing new innovative products, engaging large untapped user communities into the businesses and enhancing customer satisfaction and retention to name the few. Where do web 2.0 and enterprise meet (mashup)? We will only be able to answer this question if we understand underlying set of principles of web 2.0 and try to put all web 2.0 blocks together in the enterprise environment.
First lets discuss the core principles of web 2.0. According to Tim O'Reilley, web 2.0 are networked applications that leverage network effects. What is "Network Effect"? It is a situation or effect in which a product or service becomes more valuable as more people use it. It is increasingly focused towards engaging large user communities into the network with new products and services, strengthening the network with shared knowledge pool and collective intelligence, and leveraging the web into business strategies, products and services. Then what is problem with widespread adoption of web 2.0 in an enterprise? We have all its constituents; audience, web, knowledge. The fourth quadrant i.e. product and services, depend and leverage the other three constituents and enable in shaping the new business strategies and opportunities with web 2.0.
Then why are the enterprises not moving as fast as they should have been in adopting web 2.0? Web 2.0 is more than just products, people, knowledge and web, it is also about processes and culture i.e. shift in power and control. Enterprises will have to change the way they do business to take strategic advantage of the web 2.0. It will not be easy to formulate a web 2.0 strategy without changing underlying processes and power switch. It will require an enterprise widespread and dynamic changes since web 2.0 approaches will require self assessment, introspection, risk and new strategic alignment. Web 2.0 is basically a disruptive model that may derail old platforms and business models. Web 2.0 advocates moving away from command and control towards collaboration and teamwork, from push to pull model, from process-centric to people-centric business model.
Even in the presence of directives from top management for enabling this change, enterprises are still unable to implement or deploy the web 2.0 apps? My 2 cents. The single biggest challenge here seems to be the employees. The sheer numbers here present a daunting task of getting them at an equal level of understanding of the new technology and its strategic advantages. It is a challenge to educate them and for many leaders, web 2.0 shift is thus beyond their scope and mandate. Avoiding risks and taking the path of incremental improvements then becomes the easier alternative.
Many companies have therefore adopted web 2.0 principles not as a business strategy but more as an experiments to get on the web 2.0 technology map. These companies are plying low risks strategies and trying to gauge its adoption with respect to business model and corporate culture. It will be interesting to see how many companies deploy web 2.0 as business strategy and change their internal culture, because that is when they take full advantages of web 2.0 principles.
The next challenge is where exactly to apply web 2.0 principles. According to research and surveys, the biggest reasons for widespread adoption of web 2.0 are to cut costs and increase revenue. Nothing new, lets find more. About 80% of companies surveyed see the collaborative aspects of Web 2.0 as a way to increase corporate revenue and/or margins. As a cost-reducer, 30% of companies expect Web 2.0 tools to trim the most in customer-service and support costs. As for increasing revenue, 40% of companies expect web 2.0 will help in acquiring new customers and 25% in product innovations. Generally perception is that collaboration is single greatest reason for web 2.0 adoption within the corporate. So far the largest implementations of web 2.0 are wikis and blogs that have been adopted as next generation collaboration tool.
There are two facets of an enterprise - internal and external. Internal apps are for their employees, internal communication, knowledge sharing and product innovation. External apps are for their customers and partners, marketing and sales, product development, customer services and retention, and new opportunities.
I will drill more into these facets and how web 2.0 can serve them. These apps may use same technologies but differ from how they are provisioned and used. I will start with internal apps in my next post and then discuss the external apps of the organization with reference to web 2.0 in subsequent posts.
Please follow the links below for rest of the series:Mashup - Web 2.0 with Enterprise (Part 2)
Mashup - Web 2.0 with Enterprise (Part 3)
Mashup - Web 2.0 with Enterprise (Part 4)
Friday, January 18, 2008
Knowledge Management Strategy - Web 2.0 Prespective
How web 2.0 initiatives has impacted knowledge management strategies of companies? How companies are adopting and adapting to the new KM generation options available out there from the web 2.0 world?
Initially people had rejected Web 2.0 as merely a buzz and marketing jargon. But as the new applications evolved and benefits became apparent, people started adopting web 2.0 seriously. Now CEOs and CIOs are openly advocating using web 2.0 in all spheres of their businesses and seeking new business opportunities, greater collaboration and more knowledge sharing across the enterprise. Though knowledge management talks about both explicit and tacit knowledge, traditional knowledge management was much heavily inclined in the favor of explicit knowledge as opposed the tacit knowledge. Knowledge management experts have always been trying to advocate more balance approach towards knowledge sharing and collaboration and web 2.0 has provided them with tools and technologies to press their need. Knowledge management and web 2.0 are natural partners in the new web paradigm.
Collaboration is key component of knowledge management which involves active participation of employees, partners and customers. Web 2.0 advocates collaboration and communication through giving up central control, collective intelligence, empowerment and active participation. Collaboration is extended to groups, communities and network building. There are various tools and technologies that provides opportunities and values to the business as collaboration vehicle.
Content Management (CMS) provides for effective creation, management and deployment of the enterprise content. The content published out CMS, can be accessed, repurposed and distributed in real-time. But content is created and management by handful of content writers that provides a contraint in itself. Web 2.0 advocates collective intelligence, information to be created and accesses by everyone at anytime from any device. Time is opportunity and no one has time to wait for information to be available. Everyone needs information that they want, right there, right when they need it. Wikis and Blogs are the great alternative solutions. There are used across the enterprises for both internal and external information sharing. Blogs have become effective tools for knowledge sharing and distribution. Wikis and Blogs also provide for effective feedback mechanism though commenting, rating and trackbacks. Wikipedia has replaced encyclopedia through shear collective content creation and management. The enterprises are trying to replicate the success of wikipedia by introducing enterprise wide knowledge repository using wikis. I am not surprised if you see Ciscopedia, micropedia or Oraclepedia in very near future.
Taxonomy provides effective way for organizing, searching and navigating the enterprise content. There is so much of content created every day within the enterprise and finding taxonomy place holder for the each content piece is getting harder everyday. Search engine provides taxonomy classifier which can automatically find taxonomy for the content. But it requires an enterprise wide taxonomy to start with. More so often, business do not have enterprise wide taxonomy for various reasons (outside scope of this post). Web 2.0 propose folksonomy which is collective building of taxonomy. It provides the readers the ability to create tags for content pieces so that it can be accessed faster and better.
Portals provides facade to all information available within the enterprise. It is single point of access to the entire knowledge base of the enterprise. Portal requires training to end users because of its functionality and not to intuitive interface. Web 2.0 propose intuitive rich user interface and experience. It advocates active user participation, self learning and minimal training.
Web 2.0 is not just a technology but it economic, social and technology trends for next generation of the Internet. It is any networked application that explicitly leverage network effect. The next generation of knowledge management tools aligns with new trends of Web 2.0. The enterprise technology strategist should take a look at web 2.0 principles and emerging initiatives before defining strategies for the knowledge management initiatives.